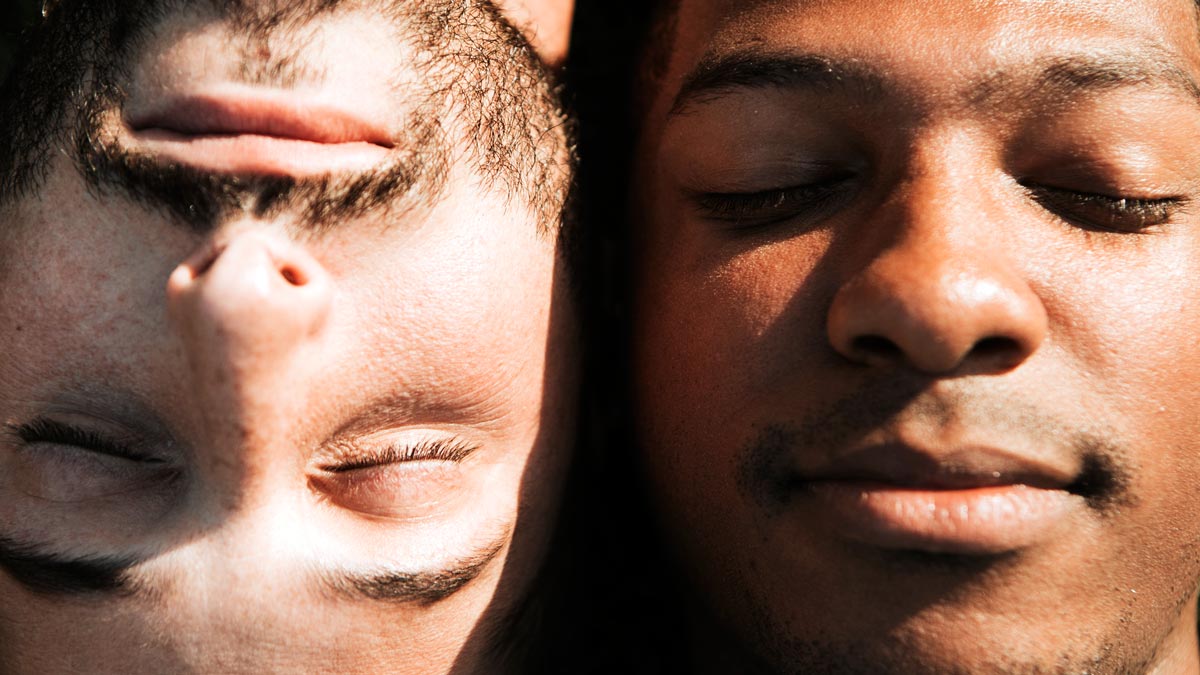
The ugly truth about Grindr and exclusion-based dating
Exclusion-based dating has long been a widely embraced norm for apps and services like Grindr, Scruff, and Tinder.
Filters enable daters to screen candidates based on factors like race. This has inevitably fed into an existing hierarchy of desirability.
As many a gay man can attest, the sexual economy of dating apps and services is one in which “White” is usually coded as most desirable. Those with intersectional identities are usually granted a lower rank.
Dating thus is not a level playing field. Rather, it mirrors the inequalities of broader society. In this case, it has been divided along the lines of attentional “haves” and “have-nots”.
“Preferences” as a result have become a mere byword for prejudice, with countless daters openly rejected on the basis of their race or some other—often superficial—trait.
Given the history of gay men being condemned for their identity, it is tragic that we now perpetuate this shaming cycle through the exclusion of our fellows.
Table of contents
The end of exclusion-based dating?
The killing of George Floyd in 2020 sparked a groundswell of support for the antiracism movement.
As #BlackLivesMatter protests rocked the globe, dating services that had formerly endorsed racial exclusion-based dating appeared to change their tunes.
Some announced they would be removing ethnic and race filter options. Others declined, citing the longstanding motivation for preference filters: maximizing user choice. (Choice which I’ve argued is largely an illusion.)
Such changes could be taken as a mark of progress. They may have also just been virtue signaling.
When the powers-that-be make a concession to the oppressed, more often than not it is less a concession than a convergence of interests. The timing of this decision suggests as much.
Arguably, little has since changed in the wake of the racial filter rollback. Identity-based pecking orders remain as entrenched as ever.

How dating apps encourage exclusion
The popularity of dating apps and services depends upon their promise of greater ease and convenience, but also the pleasures offered by gamification. Exclusion-based dating exists because app design reinforces this pattern.
To explain: sorting through the sheer number of prospects on dating services requires a process of elimination. Filters present themselves as the logical conclusion.
And so users are funneled into a preset selection of behaviors, responding to each candidate on a binary yes/no basis.
Sorting through an ocean of romantic/sexual options demands significant mental energy. Our brain quickly learns to conserve that energy by autonomizing the process.
A careful profile survey is refined into a reflexive swipe. Preferences shift into hard “no”s. Full sentences degrade into monosyllables.
The apps positively reinforce our continued engagement with this pattern through instant notifications. Flashy animations and sounds signal success, assuring us that whatever we are doing must be right.
We in turn interpret our behaviors as winning strategies, leaving us less prone to questioning our own biases.
Overcoming exclusion-based dating
Studies show that unconscious bias is almost universal. Biases often reflecs those held by wider society; racism on dating apps are often a product of widespread systemic racism.
Left unchallenged, biases color our perception of the world. They fledge into prejudice, promoting “isms” such as ableism, ageism, classism, ethnocentrism, heterosexism, transphobia, and sexism.
The first step to overcoming biases is awareness. If you suspect you are prone to a particular bias, consider taking a free implicit bias test.
The second step is introducing information that directly conflicts with our automatic patterns of thinking about a particular group.1
Consider writing a letter to yourself, exploring the reasoning behind a specific bias or prejudice. Describe the experiences that may have given rise to it. Find possible flaws or contradictions in your biased belief system.
Weigh your dating preferences against your values. Do the two align, and if not, what then are you willing to do to address it?
Revising any attitude, belief, and response involves some mental effort. Dating apps on the other hand encourage us to suspend “intention, attention, and effort”2 for the sake of convenience and efficiency—then reward us for doing so.
Giving into automaticity results in us falling back on old habits. Like a car following grooves and ruts in the road, we will very quickly “tramline” our way back into bias.
Without self-reflection, we are at the mercy of our worst instincts. Only by developing awareness about our own thinking can we escape the toxic hold of exclusion-based dating.

Essy Knopf is a therapist who likes to explore what it means to be neurodivergent and queer. Subscribe to get all new posts sent directly to your inbox.
- Devine, P. G. (1989). Stereotypes and prejudice: Their automatic and controlled components. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56(1), 5–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.56.1.5
- Devine, 1989, p. 16
© 2024 Ehsan "Essy" Knopf. Any views or opinions represented in this blog are personal and belong solely to the blog owner and do not represent those of people, institutions or organizations that the owner may or may not be associated with in professional or personal capacity, unless explicitly stated. All content found on the EssyKnopf.com website and affiliated social media accounts were created for informational purposes only and should not be treated as a substitute for the advice of qualified medical or mental health professionals. Always follow the advice of your designated provider.